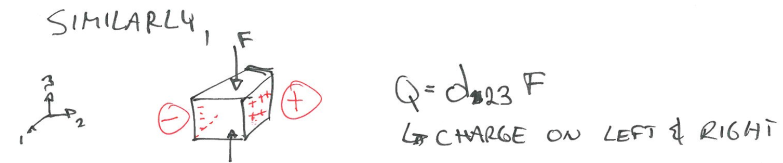Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric Effect
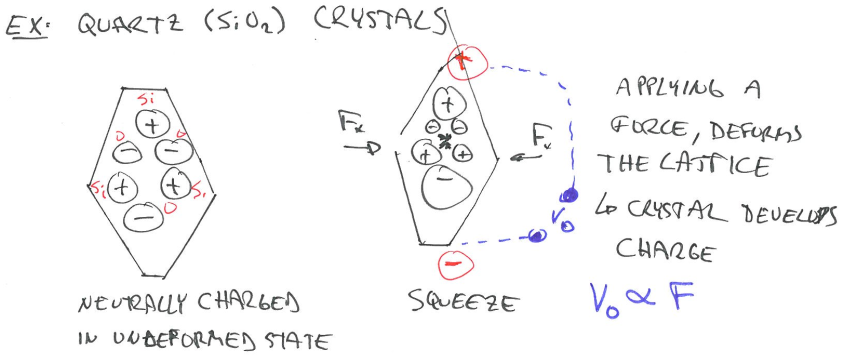
Piezoelectric Effect is the ability of certain materials to generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress. The word Piezoelectric is derived from the Greek piezein, which means to squeeze or press, and piezo, which is Greek for “push”.
- When subjected to a mechanical force, some crystalline materials become electrically polarized.
- Similarly, if we apply a voltage (charge) to the crystal, it will deform mechanically. - “Inverse” piezoelectric effect.
- Naturally occurring crystal materials have limitations when it comes to sensing: fragility, shape possibilities. (For example, before we squeeze the crystal enough to have measurable voltage, it might already broken.)
- We can, however, make our own metal oxide-based piezoelectric ceramics.
Piezoelectric Constant
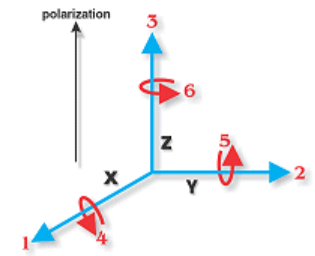
The response of piezoelectric elements is highly directionally dependent (anisotropic): 1) direction of polarization 2) direction of applied force
- This is the standard frame of reference
- All constants are given in: $\propto_{AB}$
Piezoelectric sensors
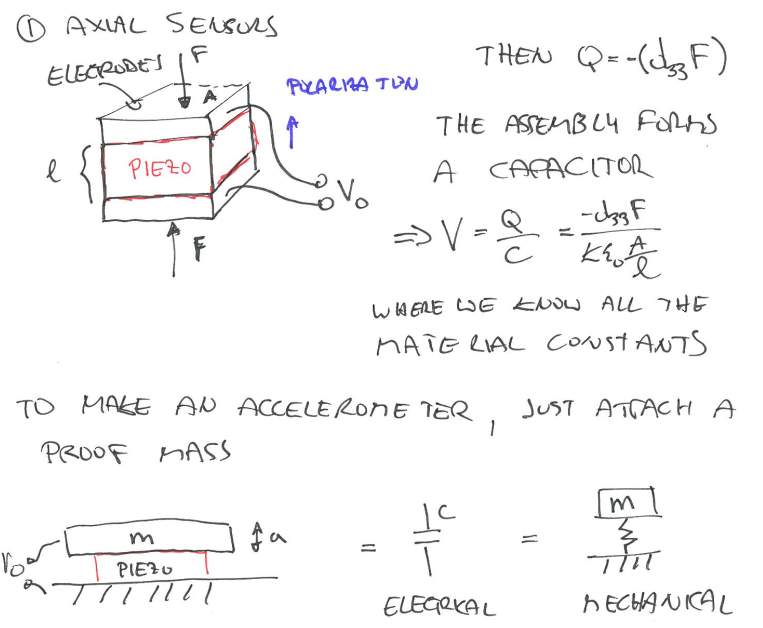
There are 2 common types of piezoelectric sensors: 1) Axial 2) Flexural
This is my notes from the class I am taking “CEE 575 Infrastructure Sensing” offered by Prof. Branko Kerkez at University of Michigan.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.